|
|
|
|
Family: Boraginaceae
[Cordia ovalis R.Br. ex A.DC.] |
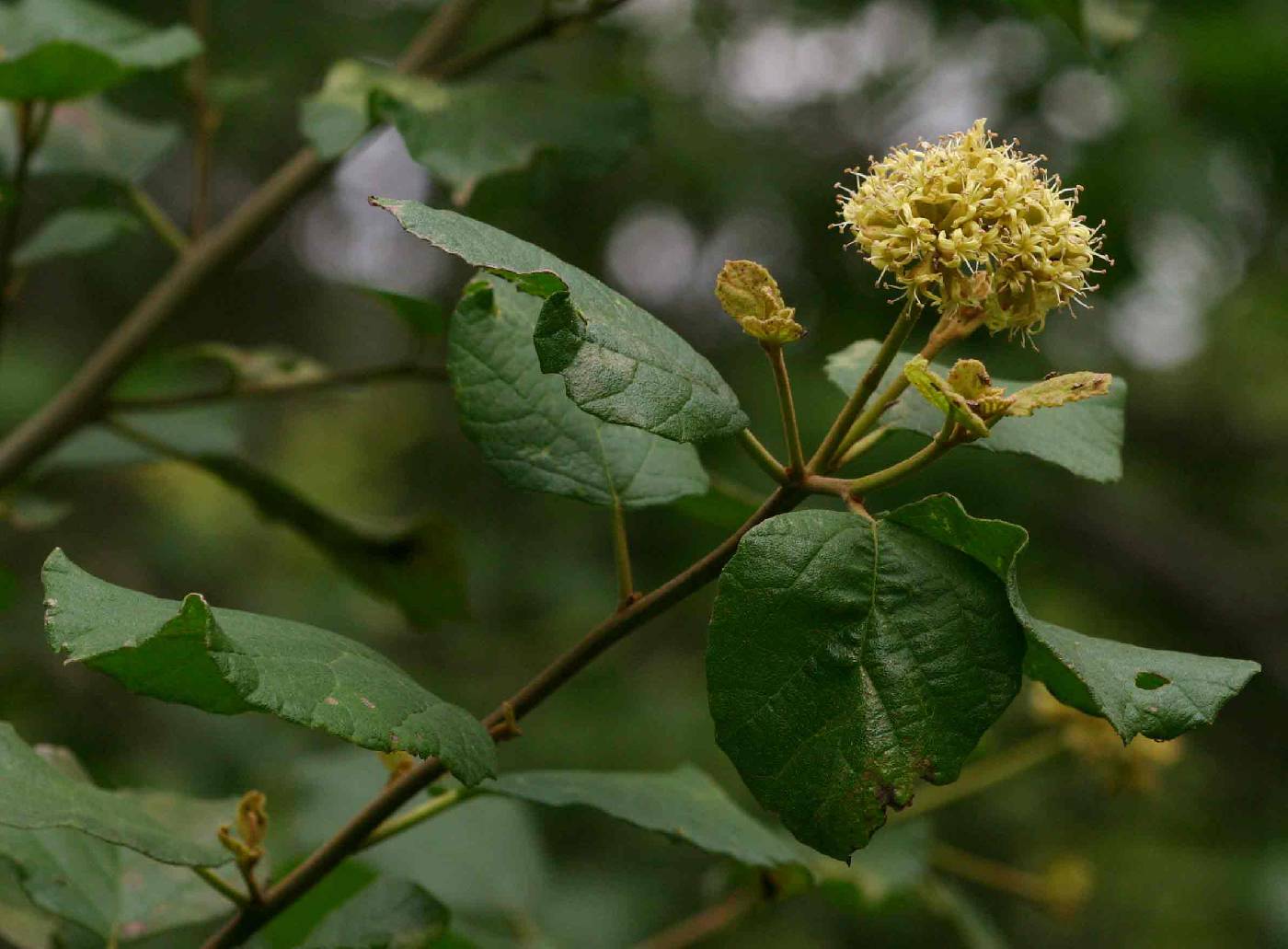
Shrubs or trees 6-12m tall with alternate, simple roundish leaves that are rough on the upper surface and have soft rust-colored hairs on the lower surface. The flowers are fragrant and in tight clusters. The calyces and pedicels are covered with yellowish hairs. The corolla has 4-5 petals that are united in their lower portion to form a tube while their upper halves curve outwards, exposing the reproductive structures. The fruits are ovoid drupes, with a fleshy yellow to orange outer part that surrounds the single seed. The are cupped at the base by the persistent calyx. Modified from the Flora of Zimbabwe and the Flora of Somalia.
A.M. Warfa (2003) Flora of Somalia 3:31-36 Plants shrubs or small trees,up to 8m tall;young branches with brownish hairs. Leaves alternate; petioles 10-25 mm long; blades 2.5-9.5 cm long, 1.9-6.7 cm wide, broadly ovate, obovate or suborbicular; base cuneate to rounded or subtruncate; tip apiculate to to rounded or emarginate; margins entire to slightly crenate; lower surface densely covered with soft, rust-colored hairs; upper surface usually very rough; lateral veins usually reaching the margins. Inflorescence dense, brownish pubescent. Flowers shortly pedicellate, fragrant, usually bisexual, rarely unisexual; calyx 4-8.5 mm long, tubular-campanulate, 4-5-lobed, densely hairy, often slightly gooved; corolla white, cream, or pale yellow, tube 4-9mm long, lobes 4-5; stamens 4-5, exserted; ovary with 1 ovule, style branches 2, 3-6 mm long. Fruiting calyces funnel- or cup-shaped, remaining attached, 6-11 mm long, 7-13 mm wide; drupes yellow orange when ripe, usually ovoid, 10-18 mm long, 5-10 mm wide. Cordia monoica grows in bushland or woodland, often in rocky places or along water courses at 15-1400 m. It is known from all regions recognized in the Flora of Somlia and from Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Sudan, tropical Africa the Arabian peninsula, and tropical Asia. The information below was obtained by searching the internet. It has not been verified. Food: The fleshy fruits are edible and have a gummy fluid. They are usually eaten raw. No information was found on their nutritional value or their use in cooking. The plants are grazed by goats and camels. Medicine: The fruits are sometimes crushed and used to treat dysentery. Their chemical constituents include P-sitosterol, D-mannitol, and flavonoid glycosides. [This information from the internet but the accuracy of the interpretation of the extract presented and the information itself needs verification. Ethanol, ethyl acetate, and petroleum ether extracts of the leaves have significant antifungal and antibacterial properties (Dhivya. A and Sivakumar R. 2014). Other: The wood of Cordia monoica is used for such things as furniture, beehives, tool handles, and water containers. Walking sticks and clubs (for use as weapons) are made from the branches. It is sometimes planted as a hedge or as an ornamental species because of its interesting branching pattern, attractive bark, and colorful fruits. Geographic: Cordia monoica is native to India and Sri Lanka and from the Sudan through eastern Africa and Madagascar to South Africa where it extends to the west side of the continent (see CJB African Plants Database for map of African distribution). Ecological: Common along water courses through semi-arid and thickets, woodlands, and grasslands. Chromosome number 2n = 70. |